Configure KMP
Android studio IDE is the dedicated IDE to consider for KMP developpement
Simply download it thanks to Jetbrain ToolBox App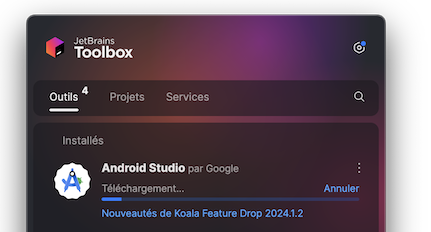
And install the latest stable version of Android Studio IDE. You can do the following to prepare it to support KMP
- Open Android Studio
- Select
Pluginstab - search for
Kotlin Multiplatformand click on install button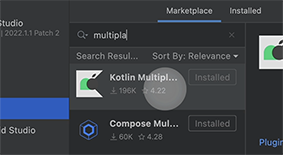
- search for
Compose Multiplatformand click on install button - restart your IDE
configuration helper
For macOS devs only,kdoctor command line interface (CLI) is available. It will help you to ensure that your computer is correctly configured for KMP development.
brew install kdoctor
kdoctor
🧪 Download the initial project

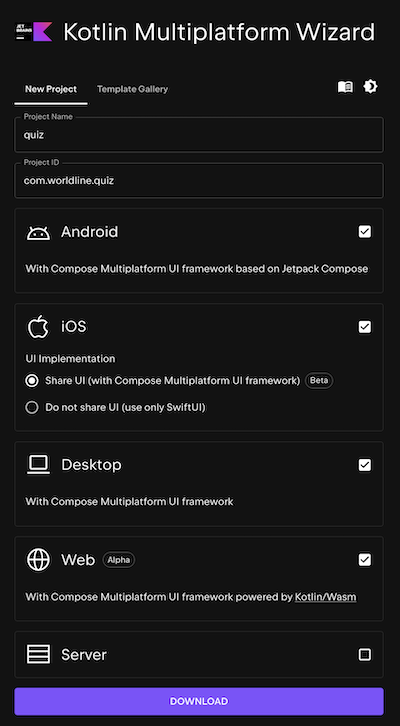
For your hand-on lab today, you can download the initial project by downloading KMP official sample for Android, iOS and Desktop & Web here: kmp.jetbrains.com
- Select : ☑️ Android ☑️ iOS ☑️ Desktop ☑️ Web
Downloadthe zip project- Open it with
Android studio
📚 A Guided tour of the sample project
Project Structure
The gradle plugin of Kotlin Multiplatform ( KMP ) organize the code thanks to 2 essential notion of Gradle/Java :
- A
Moduleis a set of classes and packages that form a complete whole with a build description filebuild.gradle. Modules have been introduced to improve safety and to make the platform more modular. - A
Source setsgive us a powerful way to structure source code in our Gradle projects. A SourceSet represents a logical group of Kotlin source and resource files.

1 - composeApp module : The crossplatform library module
A shared library module linked to all project platforms. It contains the source code common to all your supported platforms.
2 - commonMain sourceSet : Shared & multiplatform Kotlin source files
This is the place where you will code all your cross platform composables.
On the sample, your first composable function App() is already configured with a single button that display an image with a standard animation on click.
App.kt
@Composable
@Preview
fun App() {
MaterialTheme {
var showContent by remember { mutableStateOf(false) }
Column(Modifier.fillMaxWidth(), horizontalAlignment = Alignment.CenterHorizontally) {
Button(onClick = { showContent = !showContent }) {
Text("Click me!")
}
AnimatedVisibility(showContent) {
val greeting = remember { Greeting().greet() }
Column(Modifier.fillMaxWidth(), horizontalAlignment = Alignment.CenterHorizontally) {
Image(painterResource(Res.drawable.compose_multiplatform), null)
Text("Compose: $greeting")
}
}
}
}
}
3 - androidMain, desktopMain, iosMain, wasmJsMain sourceSets: KMP specific library modules
One submodule per platform, linked to the common module sources. It gives the possibility to make specific implementations of functions per platform
Platform specific source file
When you need a specific implementation for Android and iOS of getPlatform() to return the platform name, KMP uses :
expectkeyword on the KMP shared library (commonMain) before functions indicating that we need a specific implementation of this functionactualkeywords on the KMP shared library specific modules (iosMain, androidMain) before functions to indicate the implementation.
For exemple on this specific template, a getPlatformName fuction is referenced on the common code and implemented specificly on each sourceset with the right platform name
platform.kt (SourceSet : commonMain)
expect fun getPlatform(): Platform
Platform.desktop.kt (SourceSet : desktopMain)
actual fun getPlatformName(): String = "Desktop"
Platform.android.kt (SourceSet : androidMain)
actual fun getPlatformName(): String = "Android"
Platform.ios.kt(SourceSet : iosMain)
actual fun getPlatformName(): String = "iOS"
More Information
On each platform sourceSet (androidMain, desktopMain, iosMain, wasmJsMain) , you can call native SDK function wrapped in Kotlin.
Ex: on Platform.ios.kt a UIDevice function is called :
UIDevice.currentDevice.systemName()
More information about platform specific functions in KMP here)
Platform specific composables
On this template a wrapper is used to use the root multiplatform composable App() on each specific sourceSet Mainclass :
onCreatecallback of anActivityfor Android- A
ViewControllerclass for iOS - ... Then you can code and declare your composables on the
App()composable to code multiplatform.
For Desktop (DesktopMain)
main.desktop.kt(SourceSet : desktopMain)
fun main() = application {
Window(
onCloseRequest = ::exitApplication,
title = "Quiz",
) {
App()
}
}
For Android (AndroidMain)
The Android app declaration with ressouces, manifest and activities A MainView android composable is created from the App() composable.
main.android.kt (SourceSet : androidMain)
@Composable fun MainView() = App()
Then the composable is declared on the activity.
MainActivity.kt (androidApp)
class MainActivity : ComponentActivity() {
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContent {
App()
}
}
}
4. for iOS (IosMain)
For iOSApp project you can open the .xcodeproj with Xcode for completion, build specific configurations
It's the same principles, a swift MainViewController that is created from the composable App()
main.ios.kt(SourceSet : iosMain)
fun MainViewController() = ComposeUIViewController { App() }
Then on the .xcodeproj, ContentView.swift convert the MainViewController into a swiftUI view.
ContentView.swift (iosApp)
...
struct ComposeView: UIViewControllerRepresentable {
func makeUIViewController(context: Context) -> UIViewController {
MainViewControllerKt.MainViewController()
}
func updateUIViewController(_ uiViewController: UIViewController, context: Context) {}
}
struct ContentView: View {
var body: some View {
ComposeView()
.ignoresSafeArea(.keyboard) // Compose has own keyboard handler
}
}
...
With those configuration you can now develop your composable in the commonMain SourceSet and deploy your app for Android, iOS and Destop targets
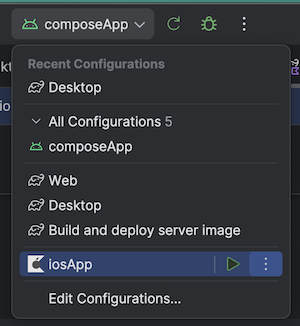
🧪 Deploy your apps
You can declare in android studio gradle run configurations
./gradlew composeApp:desktopRun -DmainClass=com.worldline.quiz.MainKt
./gradlew wasmJsBrowserDevelopmentRun #Web
Running configuration

Version Catalog
A version catalog is a list of dependencies, represented as dependency coordinates, that a user can pick from when declaring dependencies in a build script.
gradle/libs.versions.toml
[versions]
# KMP AGP/GRADLE compatibility guide
# https://wrl.li/guideagp
kotlin = "2.0.20"
agp = "8.5.0"
compose-plugin = "1.7.0-rc01"
androidx-activityCompose = "1.9.2"
navigation = "2.8.0-alpha10"
androidx-lifecycle = "2.8.0"
kotlinxCoroutinesCore="1.9.0"
kotlinx-coroutines = "1.8.1"
kotlinxDatetime = "0.6.1"
ktorVersion = "3.0.0-rc-1"
kstore = "0.8.0"
logback = "1.5.8"
android-compileSdk = "34"
android-minSdk = "24"
android-targetSdk = "34"
[libraries]
androidx-activity-compose = { module = "androidx.activity:activity-compose", version.ref = "androidx-activityCompose" }
androidx-lifecycle-viewmodel = { group = "org.jetbrains.androidx.lifecycle", name = "lifecycle-viewmodel", version.ref = "androidx-lifecycle" }
androidx-lifecycle-runtime-compose = { group = "org.jetbrains.androidx.lifecycle", name = "lifecycle-runtime-compose", version.ref = "androidx-lifecycle" }
kotlinx-coroutines-swing = { group = "org.jetbrains.kotlinx", name = "kotlinx-coroutines-swing", version.ref = "kotlinx-coroutines" }
kotlinx-coroutines-core = { module = "org.jetbrains.kotlinx:kotlinx-coroutines-core", version.ref = "kotlinxCoroutinesCore" }
kotlin-navigation = { module = "org.jetbrains.androidx.navigation:navigation-compose", version.ref = "navigation" }
kotlinx-datetime = { module = "org.jetbrains.kotlinx:kotlinx-datetime", version.ref = "kotlinxDatetime" }
ktor-serialization-kotlinx-json = { module = "io.ktor:ktor-serialization-kotlinx-json", version.ref = "ktorVersion" }
ktor-client-core = { module = "io.ktor:ktor-client-core", version.ref = "ktorVersion" }
ktor-client-content-negotiation = { module = "io.ktor:ktor-client-content-negotiation", version.ref = "ktorVersion" }
ktor-client-okhttp = { module = "io.ktor:ktor-client-okhttp", version.ref = "ktorVersion" }
ktor-client-apache = { module = "io.ktor:ktor-client-apache", version.ref = "ktorVersion" }
ktor-client-darwin = { module = "io.ktor:ktor-client-darwin", version.ref = "ktorVersion" }
#kstore
kstore = { module = "io.github.xxfast:kstore", version.ref = "kstore" }
kstore-file = { module = "io.github.xxfast:kstore-file", version.ref = "kstore" }
kstore-storage = { module = "io.github.xxfast:kstore-storage", version.ref = "kstore" }
# Web
#ktor-client-js = { module = "io.ktor:ktor-client-js", version.ref = "ktorVersion" }
# Server
ktor-server-core = { module = "io.ktor:ktor-server-core-jvm", version.ref = "ktorVersion" }
ktor-server-cio = { module = "io.ktor:ktor-server-cio", version.ref = "ktorVersion" }
ktor-server-content-negotiation = { module = "io.ktor:ktor-server-content-negotiation", version.ref = "ktorVersion" }
ktor-server-config-yaml = { module = "io.ktor:ktor-server-config-yaml", version.ref = "ktorVersion" }
ktor-server-cors = { module = "io.ktor:ktor-server-cors", version.ref = "ktorVersion" }
logback = { module = "ch.qos.logback:logback-classic", version.ref = "logback" }
[plugins]
androidApplication = { id = "com.android.application", version.ref = "agp" }
androidLibrary = { id = "com.android.library", version.ref = "agp" }
jetbrainsCompose = { id = "org.jetbrains.compose", version.ref = "compose-plugin" }
compose-compiler = { id = "org.jetbrains.kotlin.plugin.compose", version.ref = "kotlin" }
kotlinMultiplatform = { id = "org.jetbrains.kotlin.multiplatform", version.ref = "kotlin" }
kotlinSerialization = { id = "org.jetbrains.kotlin.plugin.serialization", version.ref = "kotlin" }
kotlinJvm = { id = "org.jetbrains.kotlin.jvm", version.ref = "kotlin" }
ktor = { id = "io.ktor.plugin", version.ref = "ktorVersion" }
Basic logging
A logger is provided by [Ktor client library] (https://ktor.io/docs/logging.html) for basic logs.
More advanced logging and debugging
Use can have more advanced logging and debugging thanks to third party libs such as NSExceptionKT or CrachKiOS or Kermit or Napier
✅ If everything is fine, go to the next chapter →
