1.1 JWT Overview
JWT in a nutshell
JSON Web Token (JWT) is an open standard (RFC 7519) that defines a compact and self-contained way for securely transmitting information between parties as a JSON object.
Information can be verified and trusted because it is digitally signed.
Used in URL, POST parameter, or an HTTP header.
Used to authenticate an API.
It contains all important information about an entity, meaning that no database queries are necessary and no need to save the session on the server.
What is JWT Structure ?
JWT looks like the following in its JWS compact serialization :
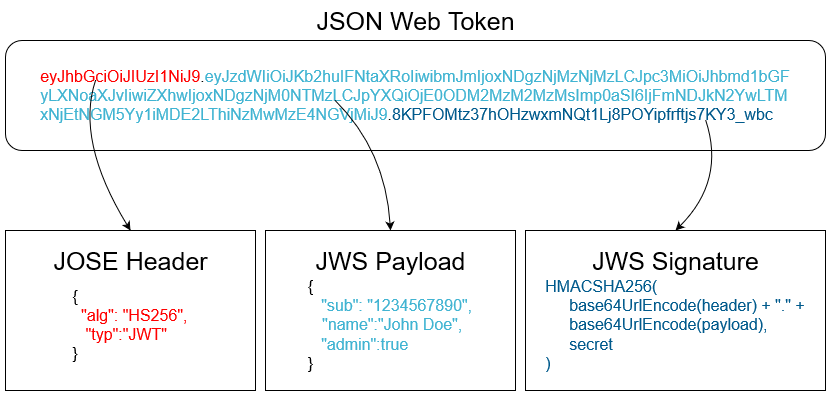
JOSE Header: (Javascript Object Signing and Encryption) Indicates to the receiver which type of signature algorithm to use for payload validation.
JWS Payload: Can contain any information but note that the content is not encrypted. So any information that you put in the token is readable by anyone who intercepts it. It is possible to use JSON Web Encryption (JWE) to encrypt the content of the payload which is then signed with JWS.
JWS Signature: is a MAC (Message authentication code) produced with the header, payload and the secret key.
What is a Bearer Token ?
The Bearer Token is a JWT used during an authentication process. Bearer Tokens are part of the OAuth V2 standard and widely adopted by many APIs. In the JWT authentication workflow, the bearer token becomes a signed temporary replacement for the login/password credentials. JWS Payload indicates the bearer standard properties for JWT Based Authentication:
issmeans the issuing entity, in this case, our authentication serveriatis the timestamp of creation of the JWTsubcontains the technical identifier of the userexpcontains the token expiration timestamp
What are JWT benefits for authentication ?
The main authentication methods are the following:
- HTTP basic authentication: relies on a simple credential scheme with username:password. They are sent in every request with risk of exposure even if sent in a secure connection. The password management is not trivial as you have to ask the user to change their passwords regularly. This method must be avoided in modern web applications, unless you add a multi-factor authentication layer.
- Authentication Cookies : CSRF and XSS can be mitigated if you always use HttpOnly flag and use signed cookies for authentication. This method is incompatible with REST as it introduces a state into a stateless protocol.
- Signature: Requires private key management. Useful for API authentication only and not adapted for browser/client authentication.
- JWT: Token based authentication widely spread today for both browser / client (SPA) and RESTful API authentication. Secure implementation is needed to avoid potential threats.
JWT key benefit is to allow the possibility to separate the Authentication logic from the Application Server.
The Application servers become safer and faster by delegating authentication to a third party server that can be one of the following:
A centralized in-house custom developed authentication server.
A commercial product like LDAP capable of issuing JWTs.
A completely external third-party authentication provider such as for example OAuth.
Another benefit is to make the application server completely stateless and no need to store password digests in application server database.