3.4 XSS Protection in Angular
What are the XSS defense mechanisms available in Angular ?
Angular Built in defense
The good news is that Angular treats all users inputs as untrusted data by default.
Therefore, it has an XSS defense by default.
Contextual escaping

Angular displays any input (malicious or not) as plain text on your webpage.
It won't interpret the input as HTML (for example in comments) if you don't explicitly tell him to.
Input Sanitization
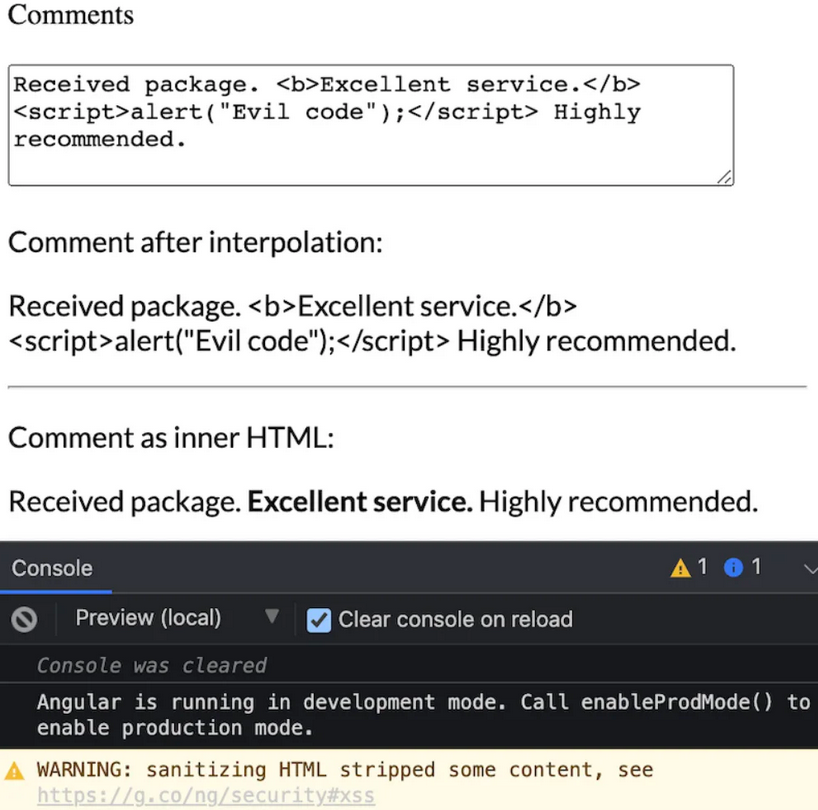
Use angular properties to bind user inputs:
[innerHtml]: binds html tags[style]: binds CSS attributes[href]: binds dynamic links
Angular will interpret the bound inputs if you explicitly use the corresponding property.
Angular automatically recognizes <script> tags as unsafe and removes it. A warning appears in the browser console to notify you if Angular has sanitized an input value.
Input Sanitization Bypassing
WARNING
⚠️ Use with care ⚠️
Sometimes application need to include executable code, display an iframe from an url or construct potentially dangerous urls...
⚠️ You must discuss this use case with your Security Officer before going further. ⚠️
If you really need to use validated user input in your application, you must mark it as trusted input.
You can use the byPassSecurityTrust...() functions from the DomSanitizer class:
abstract class DomSanitizer implements Sanitizer {
abstract sanitize(context: SecurityContext, value: string | SafeValue): string | null
abstract bypassSecurityTrustHtml(value: string): SafeHtml
abstract bypassSecurityTrustStyle(value: string): SafeStyle
abstract bypassSecurityTrustScript(value: string): SafeScript
abstract bypassSecurityTrustUrl(value: string): SafeUrl
abstract bypassSecurityTrustResourceUrl(value: string): SafeResourceUrl
}